Vitamin C, a crucial nutrient for overall health, demands regular consumption to stave off deficiency. While scarcity is relatively uncommon in developed nations due to the accessibility of fresh foods and fortified supplements, it still affects around 7 percent of American adults. This deficiency is often tied to various risk factors, including poor diet, alcoholism, anorexia, severe mental illness, smoking, and dialysis.
Identifying vitamin C deficiency involves recognizing both subtle and severe symptoms. Here are the 8 most common signs that your body might be craving more of this essential nutrient:
1. Weight Gain:

Early research indicates a link between low vitamin C levels and increased body fat, particularly in the abdominal region. This vitamin may also influence how the body metabolizes fat for energy.
2. Sluggish Wound Healing:

When vitamin C levels drop in the blood and tissues after an injury, it hampers the production of collagen, a pivotal protein in skin repair. Additionally, vitamin C aids neutrophils, white blood cells crucial for infection resistance.
3. Bleeding Gums, Nosebleeds, Bruises:
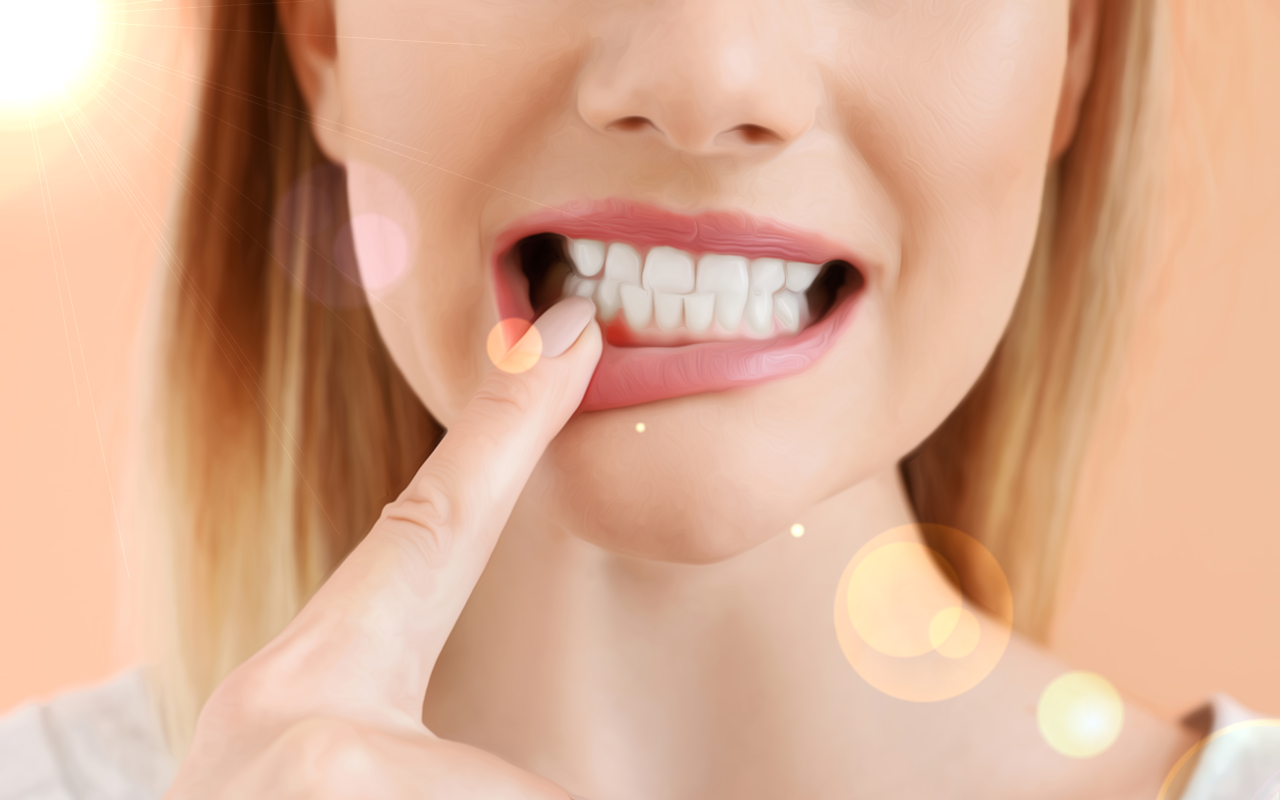

Vitamin C’s role in maintaining healthy blood vessels and promoting blood clotting is evident in gum health. Studies show that individuals with gum disease experienced reduced bleeding after incorporating grapefruit into their diet.
4. Joint Pain:
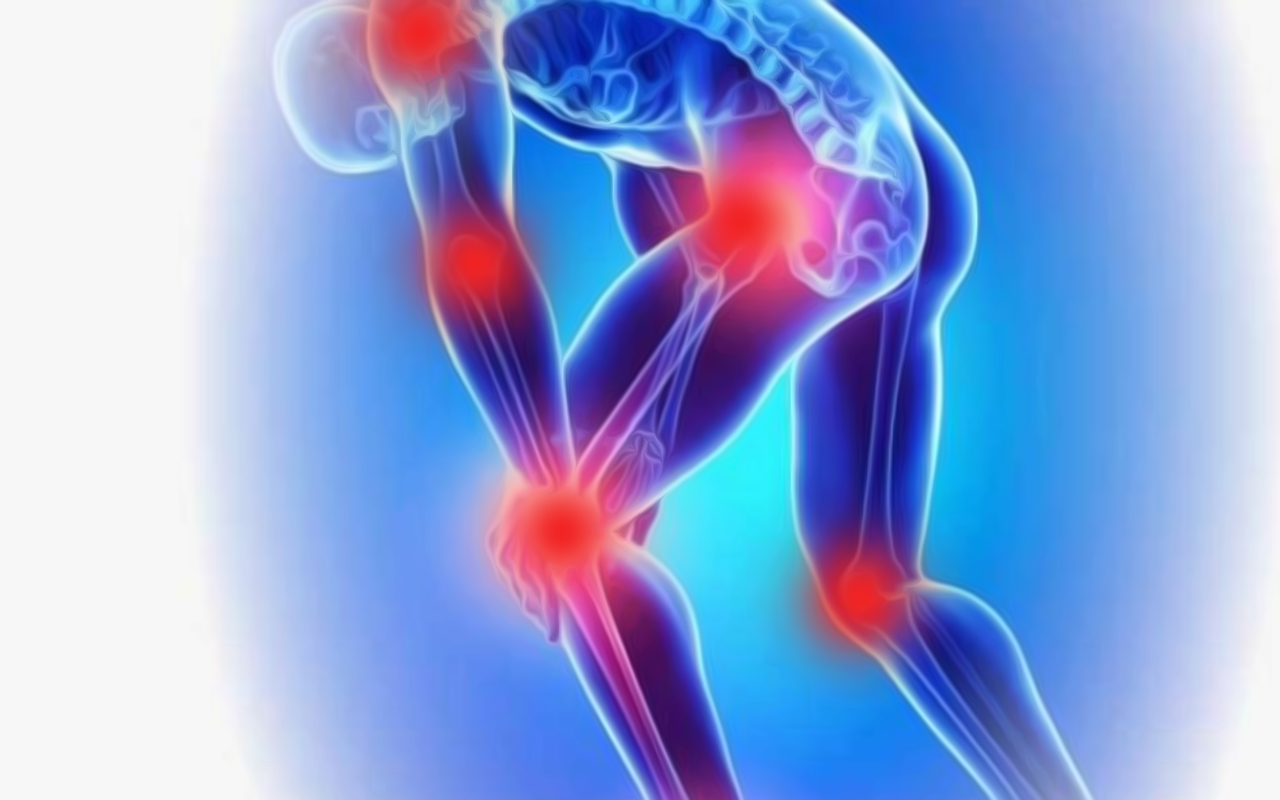
Joint pain, according to experts, is one of the earliest signs of vitamin C deficiency. As an anti-inflammatory antioxidant, vitamin C plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation.
5. Dry and Wrinkled Skin:

A diet rich in vitamin C contributes to smoother, softer skin. As an antioxidant, vitamin C protects the skin from free radicals that can damage oils, proteins, and DNA.
6. Weak Immunity:

Given its vital role in immune system functions, a deficiency in vitamin C can lead to increased susceptibility to illnesses. Some evidence suggests that vitamin C may offer protection against pneumonia, bladder infections, heart disease, and certain cancers.
7. Loss of Vision:

Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) can progress faster without sufficient vitamin C, antioxidants, and certain minerals. While vitamin C from food sources may help prevent cataracts, further research is needed to fully understand this relationship.
8. Fatigue and Irritability:

Limited vitamin C levels have been associated with fatigue and irritability. Studies show that supplementation improved energy levels, especially in individuals with initially lower vitamin C levels.
Preventing vitamin C deficiency is simple—incorporate a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables into your diet. Golden chili peppers, kiwis, cranberries, papayas, bell peppers, oranges, kale, and spinach are excellent sources, each containing over 100 mg of vitamin C. By embracing these nutrient-rich options, you not only ward off deficiency but also support overall health and well-being.